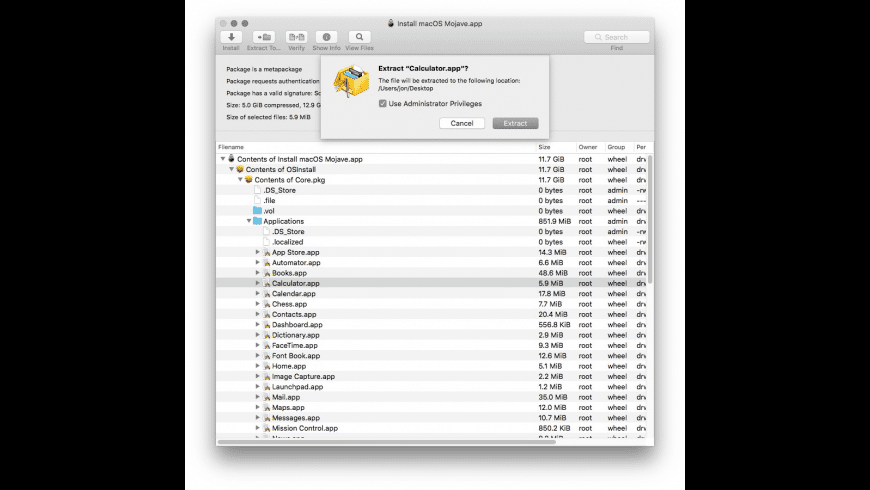
.dmg Vs .tar.gz
Dmg-01-3c2-10. Nintendo Gameboy original DMG-01 Grey Japan GB DMG-03 cord Radar Mission Box. $20.50 +$11.95 shipping.RESTORED. ORIGINAL NINTENDO GAME BOY DMG-01 HANDHELD CONSOLE.NEW GLASS LENS. $75.99. Free shipping. Gameboy Gray DMG-01 Used Works. $19.99 +$14.20 shipping. Orient Mall®New Full Parts Replacement Housing Shell Pack For Original Nintendo Game Boy(1989) DMG-01-Clear White Color(bulk packaging).
A TAR.GZ file is a TAR archive compressed with the standard GNU zip (gzip) compression algorithm. It contains one or more compressed files and is commonly used on Unix operating systems to package files, programs, and installers. Apr 10, 2016 The tar command on Linux is often used to create.tar.gz or.tgz archive files, also called “tarballs.” This command has a large number of options, but you just need to remember a few letters to quickly create archives with tar. The tar command can extract the resulting archives, too. DMG files are not zipped files, as much as they are images. They are closer to an.iso than a.zip in that they are disk images which are mountable and the contents can be compressed. A DMG therefor must also contain block data, along with the regular file attributes like Meta data and the actual data of the file.
| Original author(s) | |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | GNU Project |
| Initial release | 31 October 1992; 26 years ago |
| Stable release | 1.10 (GNU Gzip)[1] / 29 December 2018; 9 months ago |
| Repository | git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/gzip.git |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Unix-like |
| Type | Data compression |
| License | GPLv3 |
| Website | www.gnu.org/software/gzip/ |
gzip is a file format and a software application used for file compression and decompression. The program was created by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler as a free software replacement for the compress program used in early Unix systems, and intended for use by GNU (the 'g' is from 'GNU'). Version 0.1 was first publicly released on 31 October 1992, and version 1.0 followed in February 1993.
File format[edit]
| Filename extension | .gz |
|---|---|
| Internet media type | application/gzip[2] |
| Uniform Type Identifier (UTI) | org.gnu.gnu-zip-archive |
| Magic number | 1f 8b |
| Developed by | Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler |
| Type of format | Data compression |
| Open format? | Yes |
| Website | gzip.org (obsolete) |
gzip is based on the DEFLATE algorithm, which is a combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. DEFLATE was intended as a replacement for LZW and other patent-encumbered data compressionalgorithms which, at the time, limited the usability of compress and other popular archivers.
'gzip' is often also used to refer to the gzip file format, which is:
- a 10-byte header, containing a magic number (
1f 8b), the compression ID (08for DEFLATE), 1-byte of header flags, a 4-byte timestamp, compression flags and the operating system ID. - optional extra headers as allowed by the header flags, including the original filename, a comment field, an 'extra' field, and a 2-byte CRC-32 checksum for the headers section.[3]
- a body, containing a DEFLATE-compressed payload
- an 8-byte footer, containing a CRC-32 checksum and the length of the original uncompressed data, modulo 232.[4]
Although its file format also allows for multiple such streams to be concatenated (gzipped files are simply decompressed concatenated as if they were originally one file[5]), gzip is normally used to compress just single files.[6] Compressed archives are typically created by assembling collections of files into a single tar archive (also called tarball[7]), and then compressing that archive with gzip. The final compressed file usually has the extension .tar.gz or .tgz.
gzip is not to be confused with the ZIP archive format, which also uses DEFLATE. The ZIP format can hold collections of files without an external archiver, but is less compact than compressed tarballs holding the same data, because it compresses files individually and cannot take advantage of redundancy between files (solid compression).
Implementations[edit]
| Developer(s) | The NetBSD Foundation |
|---|---|
| Repository | cvsweb.netbsd.org/bsdweb.cgi/src/usr.bin/gzip/ |
| Written in | C |
| Type | Data compression |
| License | Simplified BSD License |
Various implementations of the program have been written. The most commonly known is the GNU Project's implementation using Lempel-Ziv coding (LZ77). OpenBSD's version of gzip is actually the compress program, to which support for the gzip format was added in OpenBSD 3.4. The 'g' in this specific version stands for gratis.[8]FreeBSD, DragonFly BSD and NetBSD use a BSD-licensed implementation instead of the GNU version; it is actually a command-line interface for zlib intended to be compatible with the GNU implementation's options.[9] These implementations originally come from NetBSD, and support decompression of bzip2 and the Unix pack format.
An alternative compression program achieving 3-8% better compression is Zopfli. It achieves gzip-compatible compression using more exhaustive algorithms, at the expense of compression time required. It does not affect decompression time.
pigz, written by Mark Adler, is compatible with gzip and speeds up compression by using all available CPU cores and threads.[10]
Derivatives and other uses[edit]
The tar utility included in most Linux distributions can extract .tar.gz files by passing the z option, e.g., tar -zxf file.tar.gz.
zlib is an abstraction of the DEFLATE algorithm in library form which includes support both for the gzip file format and a lightweight stream format in its API. The zlib stream format, DEFLATE, and the gzip file format were standardized respectively as RFC 1950, RFC 1951, and RFC 1952.
The gzip format is used in HTTP compression, a technique used to speed up the sending of HTML and other content on the World Wide Web. It is one of the three standard formats for HTTP compression as specified in RFC 2616. Netflix download to mac. This RFC also specifies a zlib format (called 'DEFLATE'), which is equal to the gzip format except that gzip adds eleven bytes of overhead in the form of headers and trailers. Still, the gzip format is sometimes recommended over zlib because Internet Explorer does not implement the standard correctly and cannot handle the zlib format as specified in RFC 1950.[11]
zlib DEFLATE is used internally by the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) format.
Since the late 1990s, bzip2, a file compression utility based on a block-sorting algorithm, has gained some popularity as a gzip replacement. It produces considerably smaller files (especially for source code and other structured text), but at the cost of memory and processing time (up to a factor of 4).[12]
AdvanceCOMP and 7-Zip can produce gzip-compatible files, using an internal DEFLATE implementation with better compression ratios than gzip itself—at the cost of more processor time compared to the reference implementation.[citation needed]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^Meyering, Jim (29 December 2018). 'gzip-1.10 released [stable]'. The Free Software Foundation. Retrieved 31 December 2018.
- ^The 'application/zlib' and 'application/gzip' Media Types. Tools.ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC6713. RFC 6713. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ^Deutsch <ghost@aladdin.com>, L. Peter. 'GZIP file format specification version 4.3'. tools.ietf.org. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ^Jean-loup Gailly. 'GNU Gzip'. Gnu.org. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ^'GNU Gzip: Advanced usage'. Gnu.org. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- ^'Can gzip compress several files into a single archive?'. Gnu.org. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ^'tarball, The Jargon File, version 4.4.7'. Catb.org. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ^'OpenBSD gzip(1) manual page'. Openbsd.org. OpenBSD. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ^'gzip'. Man.freebsd.org. 9 October 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ^Mark Adler (2017). 'pigz: A parallel implementation of gzip for modern multi-processor, multi-core machines'. zlib.net.
- ^Lawrence, Eric (21 November 2014). 'Compressing the Web'. MSDN Blogs > IEInternals. Microsoft.
- ^'Comparison Tool: 7-zip vs bzip2 vs gzip'. compressionratings.com. Archived from the original on 1 November 2014. Retrieved 1 November 2014.
References[edit]
- RFC 1952 – GZIP file format specification version 4.3
External links[edit]
7-Zip is a file archiver with a high compression ratio.
Download 7-Zip 19.00 (2019-02-21) for Windows:
| Link | Type | Windows | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Download | .exe | 32-bit x86 | 1 MB |
| Download | .exe | 64-bit x64 | 1 MB |
Download 7-Zip 19.02 alpha (2019-09-05) for Windows:
| Link | Type | Windows | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Download | .exe | 32-bit x86 | 1 MB |
| Download | .exe | 64-bit x64 | 1 MB |
Dmg Vs Tar Gz
License
7-Zip is free software with open source. The most of the code is under the GNU LGPL license. Some parts of the code are under the BSD 3-clause License. Also there is unRAR license restriction for some parts of the code. Read 7-Zip License information.
You can use 7-Zip on any computer, including a computer in a commercial organization. You don't need to register or pay for 7-Zip.
The main features of 7-Zip
Java Dmg Or Tar.gz
- High compression ratio in 7z format with LZMA and LZMA2 compression
- Supported formats:
- Packing / unpacking: 7z, XZ, BZIP2, GZIP, TAR, ZIP and WIM
- Unpacking only: AR, ARJ, CAB, CHM, CPIO, CramFS, DMG, EXT, FAT, GPT, HFS, IHEX, ISO, LZH, LZMA, MBR, MSI, NSIS, NTFS, QCOW2, RAR, RPM, SquashFS, UDF, UEFI, VDI, VHD, VMDK, WIM, XAR and Z.
- For ZIP and GZIP formats, 7-Zip provides a compression ratio that is 2-10 % better than the ratio provided by PKZip and WinZip
- Strong AES-256 encryption in 7z and ZIP formats
- Self-extracting capability for 7z format
- Integration with Windows Shell
- Powerful File Manager
- Powerful command line version
- Plugin for FAR Manager
- Localizations for 87 languages
7-Zip works in Windows 10 / 8 / 7 / Vista / XP / 2016 / 2012 / 2008 / 2003 / 2000 / NT.
p7zip - the port of the command line version of 7-Zip to Linux/Posix.
On 7-Zip's SourceForge Page you can find a forum, bug reports, and feature request systems.
Bin.dmg Vs Bin.tar.gz
Compression ratio
We compared 7-Zip with WinRAR 5.20.
Dmg Or Tar.gz
FILE SETS: Mozilla Firefox 34.0.5 for Windows and Google Earth 6.2.2.6613 for Windows.
| Archiver | Mozilla Firefox | Google Earth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 files 85 280 391 bytes | 483 files 110 700 519 bytes | |||
| Compressed size | Ratio | Compressed size | Ratio | |
| 7-Zip 9.35 -mx | 39 357 375 | 100% | 15 964 369 | 100% |
| WinRAR 5.20 -m5 -s -ma5 -md128m | 41 789 543 | 106% | 17 035 432 | 107% |
Compression ratio results are very dependent upon the data used for the tests. Usually, 7-Zip compresses to 7z format 30-70% better than to zip format. And 7-Zip compresses to zip format 2-10% better than most of other zip compatible programs.